Redis is an in-memory data structure store, used as a distributed, in-memory key–value database, cache and message broker, with optional durability. Redis supports different kinds of abstract data structures, such as strings, lists, maps, sets, etc.
Supported syncing
| Sync Type | Description | Supported Sync Modes | API Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Redis Cache | Sync data from any source to a Redis cache database | Upsert, Update | Redis Cache |
Connect to Redis
Go to the Destinations overview page and click the Add destination button. Select Redis and click Continue.
Connect to a Redis instance
Authenticate Hightouch to Redis with your hostname and port. If your Redis instance has authentication credentials, you can also input a username and password.
SSH tunneling
Hightouch can connect directly to Redis over the public internet or via an SSH tunnel. Since data is encrypted in transit via TLS, a direct connection is suitable for most use cases. You may need to set up a tunnel if your Redis instance is on a private network or virtual private cloud (VPC).
Hightouch supports both standard and reverse SSH tunnels. To learn more about SSH tunneling, refer to Hightouch's tunneling documentation.
Connect to a Redis cluster
Hightouch needs permission to access all cluster nodes of your Redis cluster. If your Redis cluster exists on a publicly available network, only the primary cluster node URL is required. Provide the cluster node URLs in the specified redis://<host>:<port> format.
Node address map
A node address map is a mapping between the addresses in the cluster and the addresses the client should connect to. This is useful when connecting to a cluster running on a different network than the client. For more information on node address maps specifically, refer to node-redis' documentation.
To get the addresses of your Redis cluster nodes, run CLUSTER NODES in your cluster. Refer to the Redis documentation for more details.
A common use case of node address mapping is connecting to AWS ElastiCache. To access ElastiCache resources through Hightouch, you will need to follow the instructions defined in this AWS tutorial to create a NAT instance in the same VPC as your ElastiCache instance, but on a public subnet. This NAT instance will need to forward a port to each Redis cluster node. Ensure that you can successfully connect to your Redis cluster through the NAT instance.
When configuring your connection from Hightouch, construct the Redis cluster node URLs by using the publicly accessible IP address of your NAT instance with the corresponding ports. Then, map each cluster node address to the corresponding public address in the node address mapping section.
Connect over a private network
If you have a Redis cluster running on a private network with no publicly accessible endpoints, you will need to create a SSH tunnel to each cluster node.
To get the addresses of your Redis cluster nodes, run CLUSTER NODES in your cluster. Refer to the Redis documentation for more details.
Provide the URL for each cluster node, and map it to its corresponding SSH tunnel.
Sync configuration
Once you've set up your Redis destination and have a model to pull data from, you can set up your sync configuration to begin syncing data. Go to the Syncs overview page and click the Add sync button to begin. Then, select the relevant model and the Redis destination you want to sync to.
Syncing to a cache database
Hightouch supports syncing keys and members to Redis.
Syncing keys
Keys identify, store, and retrieve data. Each key in Redis maps to a corresponding value.
Supported commands
| Command | Description | Supported Sync Modes | API Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
SET | Set key to hold the string value. | Upsert, Update | SET Command |
HSET | Set specified fields to their respective values in the hash stored at key. | Upsert, Update | HSET Command |
SADD | Add specified members to the set stored at key. | Upsert | SADD Command |
GEOADD | Add specified geospatial items (longitude, latitude, name) to the specified key. | Upsert | GEOADD Command |
Record matching
To match rows from your model to records in Redis, you need to select the model column that contains values that match the Key field in Redis.
Field mapping
You can sync columns from your source to custom fields in Redis.
Time to live (TTL)
You can set an expiration for the keys that you are syncing to Redis by setting a TTL value. This value is the amount of time in seconds that the keys will exist in Redis before they're automatically deleted.
Delete behavior
The delete behavior you select dictates what to do when a row no longer appears in your model's query results. You have the following options:
| Behavior | Description |
|---|---|
| Do nothing | Keep the key in Redis with its fields untouched |
| Clear | Keep the key in Redis, but set mapped fields to empty |
| Delete | Remove the key from Redis |
Syncing members
Members are used for managing sorted sets in Redis.
Supported commands
| Command | Description | Supported Sync Modes | API Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
ZADD | Add all specified members with the specified scores to the sorted set stored at key. | Upsert, Update | ZADD Command |
GEOADD | Add specified geospatial items (longitude, latitude, name) to the specified key. | Upsert | GEOADD Command |
Record matching
To match rows from your model to records in Redis, select the model column that contains the unique member values of each element of the sorted set in Redis.
Field mapping
The fields available for mapping depend on the command that you've selected.
Delete behavior
The delete behavior you select dictates what to do when a row no longer appears in your model's query results. You have the following options:
| Behavior | Description |
|---|---|
| Do nothing | Keep the member in Redis with its fields untouched |
| Clear | Keep the member in Redis, but set mapped fields to empty |
| Delete | Remove the member from the sorted set from Redis |
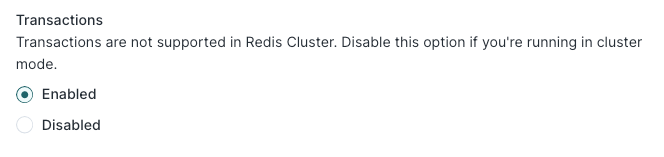
Transactions
Transactions are disabled by default when connected to a Redis cluster. You can toggle transactions for your Redis instance by configuring the options as shown.
Tips and troubleshooting
Common errors
If you encounter an error or question not listed below and need assistance, don't hesitate to . We're here to help.
Invalid argument type
This error can happen when syncing data types that aren't supported by Redis, such as null values. If your model columns contain null values, you can enable Don't sync null values to avoid syncing them.
Live debugger
Hightouch provides complete visibility into the API calls made during each of your sync runs. We recommend reading our article on debugging tips and tricks to learn more.
Sync alerts
Hightouch can alert you of sync issues via Slack, PagerDuty, SMS, or email. For details, please visit our article on alerting.
